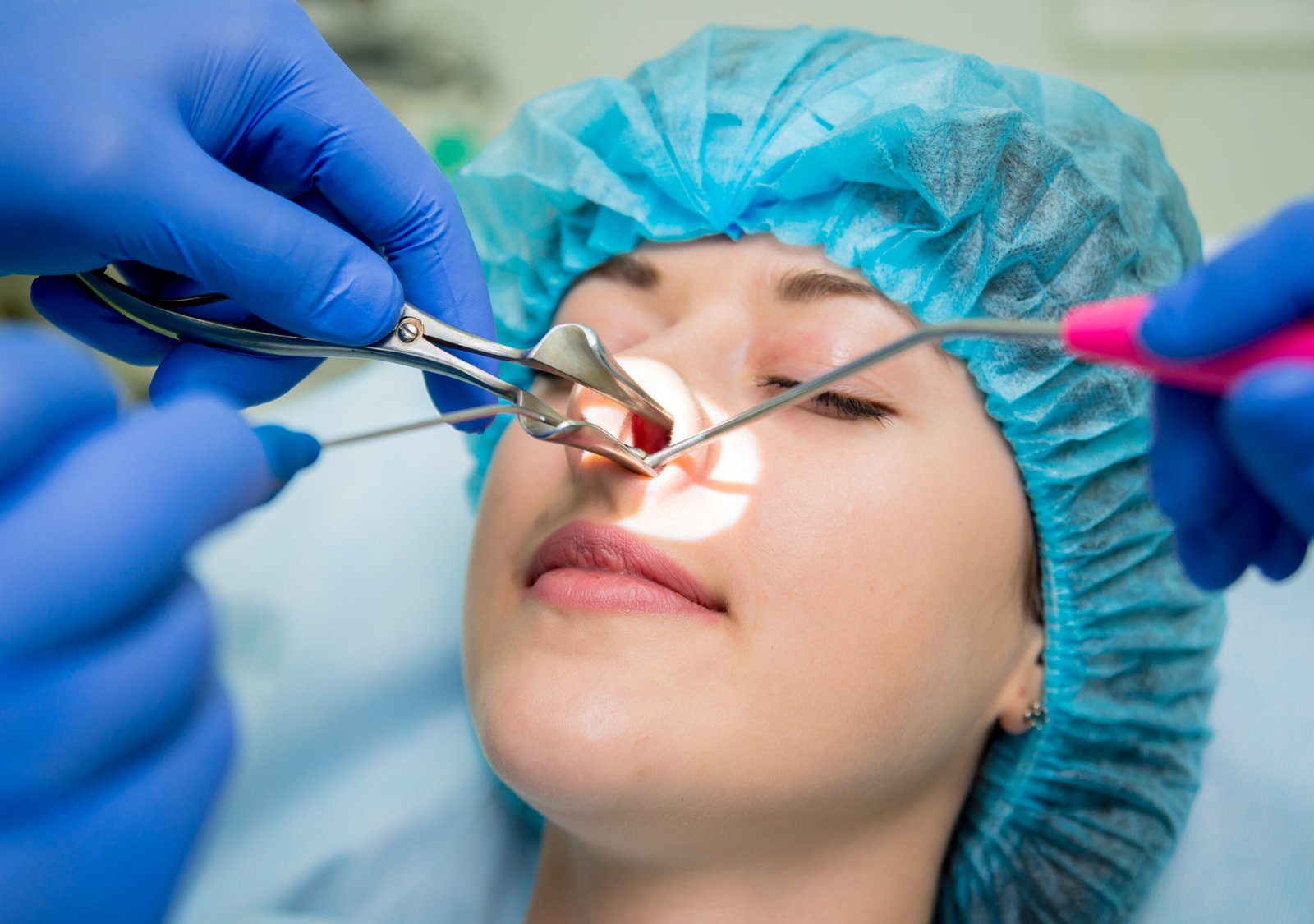
Nasal and sinus surgery is a specialized area of otolaryngology focused on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and pathologies affecting the nasal cavity and adjacent sinuses. These structures play a key role in breathing, olfaction, and filtering inhaled air, so their health is crucial to the patient’s overall well-being. A sinus surgery specialist provides advanced care and precise treatment for conditions that require surgical intervention. Surgical procedures in this area may be necessary for a variety of conditions, such as chronic sinusitis, polyps, a deviated septum, and tumors. These interventions offer radical solutions to many medical problems, improving the patient’s quality of life. Modern technologies allow for operations with minimal tissue damage and a short recovery period. Timely surgical treatment helps prevent the development of serious complications, such as the spread of infection or airway obstruction.
About the service
Nasal and sinus surgery is an important and complex area of medicine, requiring highly qualified and experienced physicians. Modern diagnostic and treatment methods allow us to successfully treat various pathologies, improving patients’ quality of life and preventing serious complications. Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus surgery procedures are used for the following conditions: chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, deviated septum, tumors, trauma, and congenital anomalies.
Preparation for surgical interventions
Preparation for surgical interventions in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses includes several stages:
- A comprehensive examination, including rhinoscopy, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to accurately determine the pathology.
- Discussion with an otolaryngologist about all aspects of the upcoming surgery, including possible risks and complications.
- General blood and urine tests, an electrocardiogram (ECG), consultation with an anesthesiologist, and other necessary tests.
Key aspects of the postoperative period
Following surgery involving the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, the patient requires some time to recover. Key aspects of the postoperative period include:
- Regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor the healing process and early detection of possible complications.
- Special procedures and exercises to restore normal nasal breathing and olfactory function.
- The use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, and pain-relieving drugs to prevent infections and reduce pain.
Endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses
Diseases of the paranasal sinuses are the most common among all ENT pathologies. Normally, the sinuses provide voice resonance, humidify and warm inhaled air, assist in olfaction, serve as thermal insulators, and secrete mucus. Long-term bacterial or fungal infections, anatomical changes in the nasal cavity (septal deformity, turbinate lining), allergies, and dental disease can lead to the development of sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). If your best ENT surgeon recommends surgery based on CT scan results, don’t be afraid. Endoscopic sinus surgery is safe and effective. It’s performed minimally invasively, without incisions or punctures. This technique is called FESS (functional endoscopic rhinosinus surgery).
Why do surgery?
Conservative treatment has not helped for many years.
Are you tired of experiencing discomfort from difficulty breathing and a stuffy nose?
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses can spread to the eye socket and brain structures.
Delicate surgery
FESS sinus endoscopy is called “gentle surgery” due to its minimally invasive nature. The idea of sinus surgery requiring puncture and mandatory aspiration is long outdated. Modern procedures are performed using an endoscope. It is inserted through the nostrils, and special instruments are used to remove inflamed mucosa and polyps. Healthy tissue is not damaged, leaving no scars. The endoscope is equipped with a camera, and the entire procedure is visible to the doctor on a monitor under high magnification.
Preparation
- Before the procedure, you must undergo a standard preoperative examination. This helps the doctor choose the optimal treatment strategy and minimize the risk of complications.
- Laboratory diagnostics – general blood test, urine test, biochemical blood test, blood coagulation system analysis, etc.
- Allergy tests (as indicated).
- MSCT of the paranasal sinuses
Rehabilitation
The FESS method allows you to go home the very next day after surgery. The Consultant ENT inpatient unit is well-equipped, so you can spend your time productively and comfortably under the supervision of doctors. After the procedure, follow your doctor’s recommendations:
- Avoid hot baths, saunas, and steam rooms;
- Limit physical activity;
- Maintain good hygiene of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
Restrictions may last up to two weeks and depend on each case. The exact duration will be determined by a doctor after an examination.
What are paranasal sinus tumors, and why do they need to be removed?
The paranasal sinuses are a system of air cavities in the bones of the face (maxillary, frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid sinuses) that are involved in breathing, humidifying, and warming the inhaled air. Growths in these sinuses (cysts, polyps, fibromas, papillomas, and sometimes tumors) can obstruct nasal ventilation, causing persistent inflammation, headaches, and congestion. Even benign growths require monitoring and often removal, as they can grow and lead to infections and complications.
Why do neoplasms occur?
Risk factors include:
- chronic inflammatory processes (sinusitis, rhinitis);
- polypoid changes of the mucous membrane;
- trauma to the nose and sinuses;
- hereditary and immunological factors;
- exposure to dust, chemical fumes, and allergens.
- The solution is surgical removal of the tumor.
The only effective method for removing this pathological growth is surgery. The procedure is performed primarily endoscopically through the nasal passages. This allows for removal without facial incisions, preserving healthy tissue, and reducing the recovery period.
Indications
- cysts or polyps in the paranasal sinuses;
- suspected tumor (based on CT, MRI, or endoscopy);
- a nasal breathing disorder that cannot be eliminated with medication.
- chronic sinusitis caused by obstruction of the sinus ostia;
- a constant feeling of pressure, pain in the sinuses, or face.
Contraindications
- acute infectious diseases;
- severe decompensated diseases of the heart and lungs;
- blood clotting disorders;
- pregnancy (for planned interventions).
Preparing for surgery
Before the intervention, an examination is carried out:
- consultation with an ENT doctor and endoscopy of the nasal cavity;
- computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses;
- general blood test, biochemistry, coagulogram;
- ECG, consultation with an anesthesiologist;
If necessary, a biopsy for histological examination.
How does the operation go?
Under local or general anesthesia, an endoscope with a high-resolution camera is inserted through the nasal passage.
- The surgeon visually determines the location of the formation.
- The neoplasm is removed with minimal trauma to the mucosa.
- If necessary, sinus sanitation is performed to prevent recurrence.
- Endoscopy eliminates external incisions and scars, and recovery is faster.
Benefits of sinus tumor removal
- Modern endoscopic access.
- No external scars.
- Minimal trauma.
- Rapid restoration of nasal breathing.
- Possibility of histological analysis of the removed material.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period usually takes 1–2 weeks. It is recommended:
- avoid overheating and physical exertion;
- perform nasal rinsing with saline solutions;
- attend follow-up examinations with an ENT doctor;
- follow individual recommendations for relapse prevention.
At the ENT private clinic, sinus tumor removal is performed by experienced ENT surgeons using advanced endoscopic technologies. We ensure precision, safety, and long-lasting treatment results.






